Understanding our Immune System
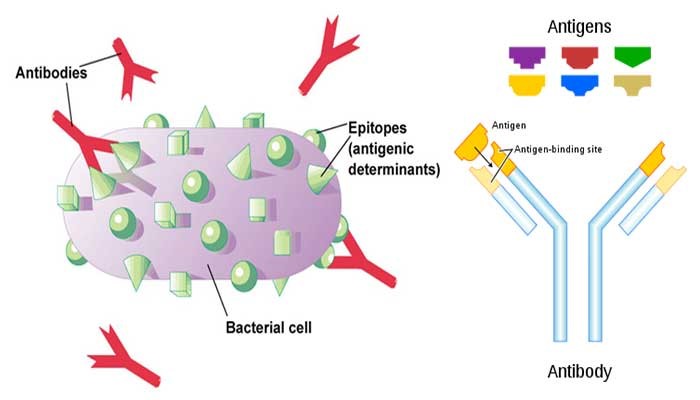
The immune system is a complex and essential component of the body’s defence against disease and infection.
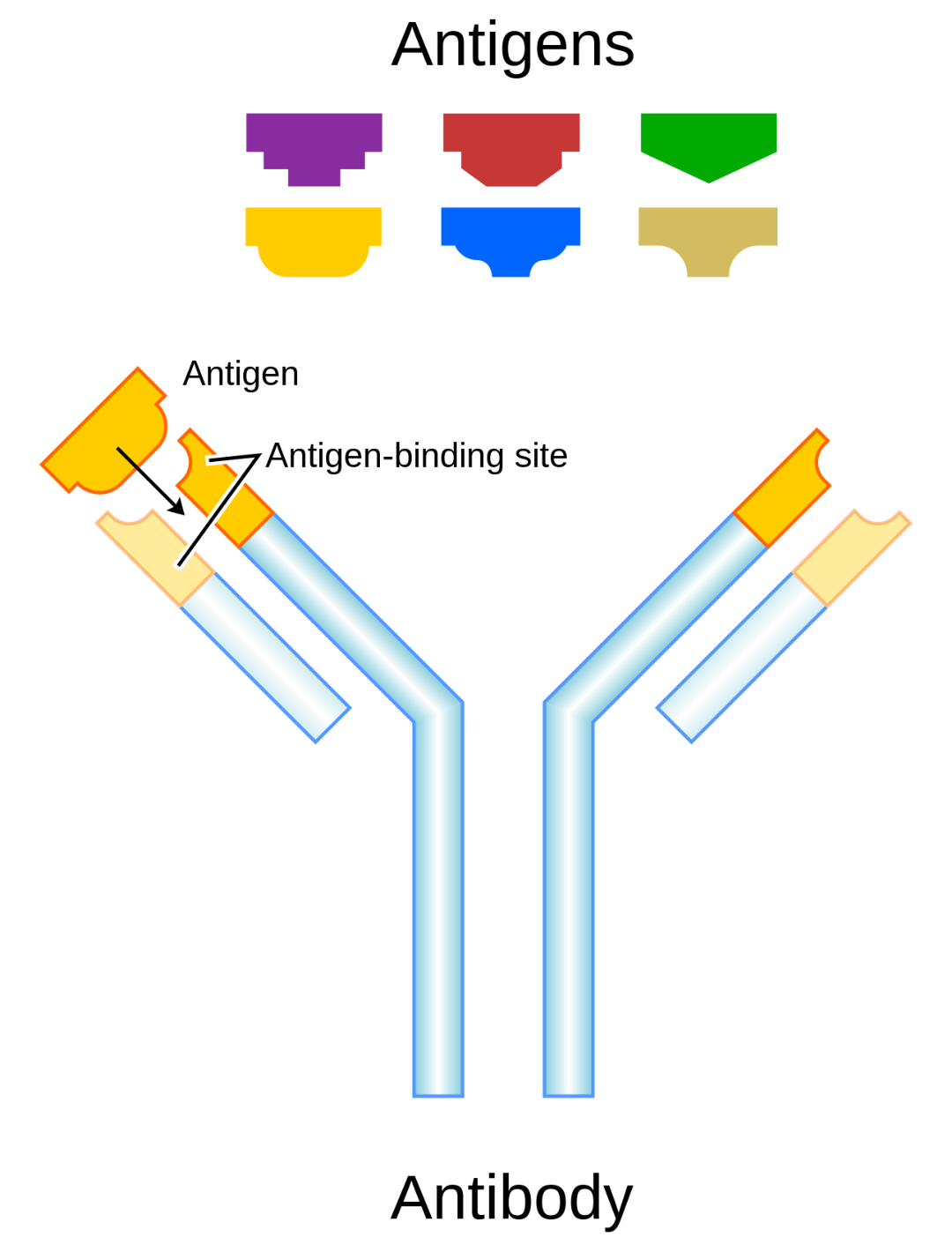
Whereas, Antibodies or immunoglobulin’s are crucial glycoprotein molecules produced by white blood cells that bind to specific antigens such as viruses or bacteria, aiding in their destruction. The immune response involving antibodies is intricate and highly specific. The various classes and subclasses of immunoglobulin’s have distinct features and target specificities, and knowledge of their structure is vital for selecting and preparing antibodies for detection applications.
Understanding immunoglobulin isotypes can offer valuable insights into the complex humoral immune response.
Two major forms of Immunoglobulin –
- Soluble Immunoglobulin – Ig or soluble immunoglobulin is a protein in the blood produced by white blood cells that recognizes and binds to specific foreign substances, aiding in their elimination. It is essential in the body’s immune response and can also be utilized as a diagnostic tool for a range of diseases and conditions.
- Membrane Bound Immunoglobulins – On the surface of immune cells like B cells, there are membrane-bound immunoglobulins. These proteins act as receptors that identify and connect with particular foreign substances like viruses or bacteria, triggering a response that can eliminate the invader. They are crucial components of the immune system, providing protection against diseases and infections.
Immunoglobulin classes (isotypes) –
Plasma cells generate a variety of antibodies that are categorized by isotype, which primarily differs in structure and antigen responses.
In placental mammals, there are five major classes of antibodies:
- IgG – Most common and abundant antibody present in blood plasma contains 75-80% IgG. It’s the only antibody that can cross the placenta barrier and provide passive immunity to a developing fetus.
- IgM – regarded as first line of defence of our immune system, as it interacts with new bacteria (pathogens) that enters the body.
- IgA – This is the most common antibody, after IgG. It is present in the blood, lymph and other body secretions such as saliva, tear, breast milk (colostrum). IgA protects body from bacterial growth & colonization.
- IgD – This makes up less than 0.5% serum antibodies. Function is still unknown.
- IgE – makes up less than 0.01% of serum antibody. It is still a potent antibody, most effective antibody against parasite infections.
Identifying individual subclasses is crucial in evaluating immune responses or primary immune deficiencies, particularly when the total concentrations of IgG or IgA are unchanged or elevated.

No comment